Red, Green, and Blue are the color gamut in TVs. As well as the white point, which determines what pure white will look like. This range includes all the colors that can be created from mixing these three primary colors.
To better understand what colors a TV can show, you can think of them as a triangle in a diagram, where each corner represents one of the primary colors.
The more saturated and vibrant these base colors are closer to the edges of the diagram, the more colors can be created from mixing them.
What is color space?
The TV color space defines the range of colors that the TV can reproduce. It determines which specific shades of red, green, and blue can be displayed.
Each color space is created based on standards that set specific color reproduction parameters.
Several color spaces exist Rec. 709, Rec. 2020, DCI-P3.
What is color gamma?
TV gamma determines how different levels of brightness are reproduced on the screen. Specifically, it controls how bright or dim the intermediate tones between the darkest and lightest colors on the screen will appear.
Adjusting gamma affects our perception of the picture because our vision does not adapt to brightness in a straightforward manner. Without proper gamma adjustment, dark moments may not be visible enough, while bright moments may be overly bright.
How are color space and color gamma related?
Color space and gamma are related. When we talk about image quality, both of these parameters play an important role. Color space determines what colors a device can reproduce, while gamma determines how those colors will be reproduced under different brightness conditions.
For a perfect image, it is essential that the device not only be able to reproduce a wide range of colors but also correctly reproduce the shades and gradations of brightness within that range. Thus, selecting the correct color space and proper gamma correction is critical to quality imaging.
Thus, color space determines what colors can be shown, and gamma determines how those colors will be shown.
What are the color spaces?
To ensure that devices reproduce colors in the same way, standards have been developed that define the range of colors that can be reproduced. This is the gamma – the color triangle.
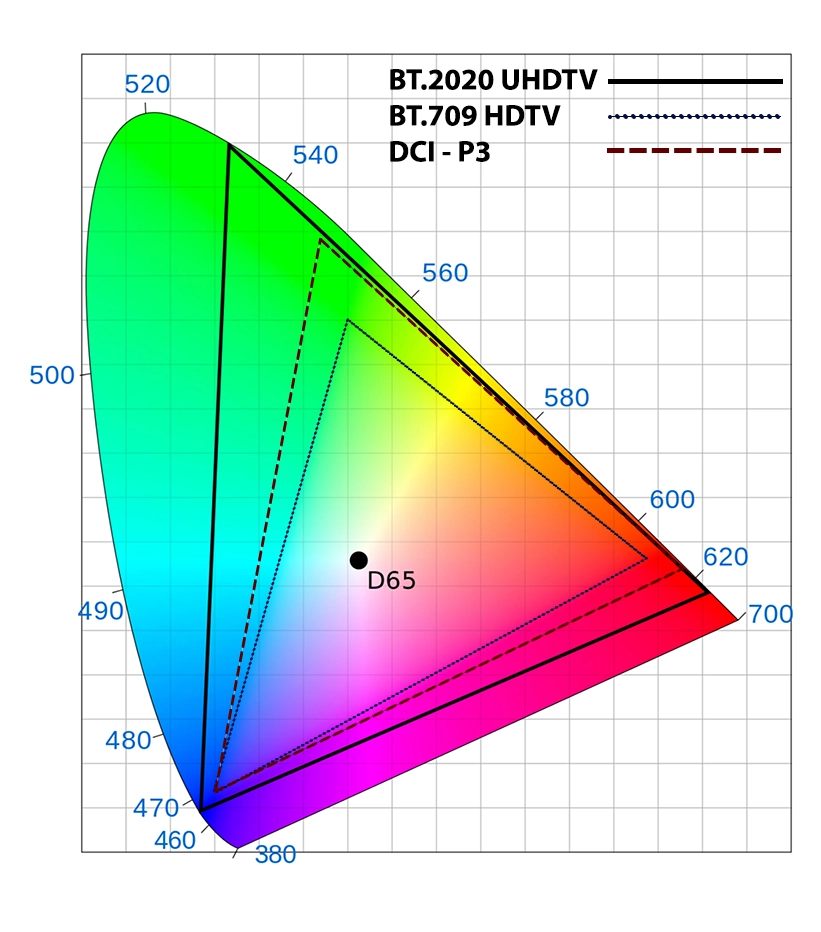
Analyzing the size of the triangle for a particular standard and its position on the chart, you can easily determine what colors a device should reproduce. The larger the triangle, the more colors will be reproduced.
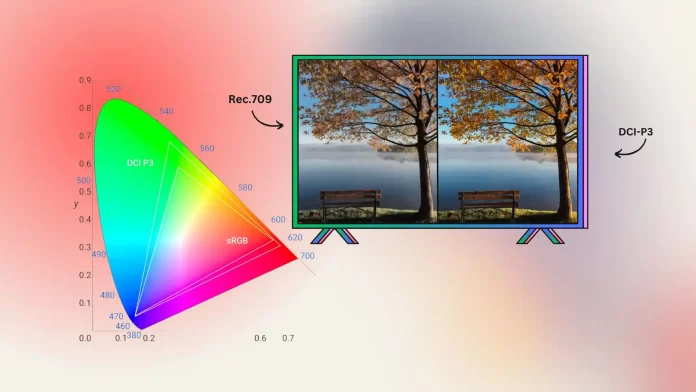
Rec. 709
Rec. 709 is the color space that has become the primary standard for HDTVs. But most modern TVs have a wider color space.
In the past, most TVs focused on the standard Rec. 709, which was introduced for HDTV. This standard covers only about 35% of the entire spectrum of colors the human eye perceives.
DCI-P3
Covers a wider range of colors than Rec. 709 and includes more saturated red and green hues. The color gamut of more budget TVs is within 80-90% of DCI-P3.
Rec.2020
Covers a significant part of the visible spectrum, but current display technologies do not yet allow this range to be fully achieved. The color gamut of high-end TVs may exceed DCI-P3, but they do not reach the Rec.2020 gamut.
How do the displays affect the color gamut?
The color space a display can reproduce depends largely on its technology and design. Consider the color spaces commonly associated with LED, OLED, and QLED TVs:
LED
The primary color space for standard LED displays is Rec. 709. Older LED TVs typically offered a medium range of colors, including moderate red, green, and blue shades.
Modern LED TVs that support HDR can often reproduce a wider range of colors supporting DCI-P3. The image then has richer and more realistic hues.

OLED
One of the main advantages of OLED displays is their ability to precisely control each pixel’s light, which allows them to achieve deep blacks and high color accuracy.
This also allows them to reproduce rich and vibrant colors, especially in the DCI-P3 range, which makes red and green hues more vibrant and saturated.
Most modern OLED TVs cover the DCI-P3 color space.
QLED
QLED TVs from Samsung and other manufacturers use quantum dots to improve LED backlights’ brightness and color accuracy.

These displays typically support DCI-P3 and take steps to reproduce Rec. 2020. Their high brightness and wide color range make them especially good for viewing HDR content.
What is the difference between color gamut and color volume?
In the field of TV and displays, the terms “color gamut” and “color volume” are often used. These concepts are different, and understanding their difference helps you better appreciate the capabilities of modern TVs.
The color gamut is the set of colors that a display can reproduce.
Color volume is a more complex concept that takes into account not only the spectrum of colors but also the brightness levels for each color.
The main difference between these concepts is that the color gamut defines a display’s colors. While color volume determines how bright or saturated those colors can be reproduced.
What does this mean for the viewer? For example, HDR TVs offer higher brightness levels, which increases their color gamut. So even if two TVs have the same color gamut, the HDR TV will have a larger color volume.

Learn more about Color Volume.
How do quantum dots affect the color gamut?
Quantum dots are used in TV displays to improve color quality and expand the color gamut.
It works in such a way that the LED backlight at the back of the screen emits a light flux that arrives at the “quantum layer.” This is what causes the dots to emit the desired color. The streams are then polarized, mixed, and different pixel colors are already formed in the liquid crystal matrix.
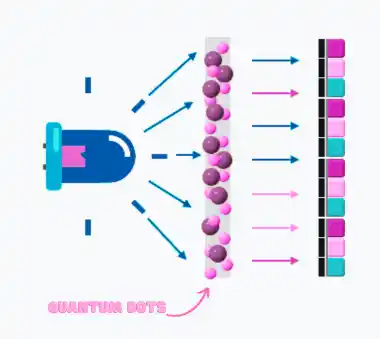
With the ability of quantum dots to emit very rich and pure colors, they can greatly expand the display’s color gamut. This allows quantum dot TVs to better meet color gamut standards such as Rec. 2020 and DCI-P3.
When quantum dots are exposed to light (usually from LEDs), they emit light of a specific color. The color that quantum dots emit depends on their size. For example, larger quantum dots emit more red light, while smaller ones emit more blue light.
How does color accuracy appear on different TVs?
Several parameters and technologies determine color accuracy on different TVs.
Color Depth
Color depth refers to the number of bits used to represent the color of each pixel. Conventional TVs often use 8 bits per color channel, which gives 256 shades of each primary color (red, green, and blue). HDR-enabled TVs may use 10 or even 12 bits per channel, increasing shades and improving color gradations.
Color Spaces
As we discussed earlier, there are different color space standards, such as Rec. 709 for HDTV, DCI-P3, and Rec. 2020. TVs that support wide color spaces can display richer and more realistic colors.

Display Technology
- OLED
These displays use organic materials that glow when current is passed through them. They are known for their deep blacks, wide viewing angles, and excellent color reproduction.
- LCD/LED
These displays use liquid crystals to control the passage of light through different colored filters. Brightness and color rendering may depend on the type of backlight.
- QLED
This is LCD technology but with the addition of quantum dots that improve color accuracy and brightness.
Color Volume
This parameter describes the display’s ability to display different colors at different brightness levels. While color gamut defines the range of colors a display can reproduce, the color volume takes into account how those colors look at different brightness levels.
QLED and OLED technologies have high color gamut because of their ability to reproduce vibrant and saturated colors at different brightness levels.
Contrast Ratio
This is the ratio of the brightest white to the darkest black that the display can reproduce. A high contrast ratio usually corresponds to a clearer and more vivid image.
OLED TVs are known for their exceptionally high contrast ratio.
This gives them an advantage over technologies such as LCD/LED, where the backlight can penetrate through the pixels even in the darkest areas of the picture.